0
item(s)
Cart is empty
|
Home
::
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis
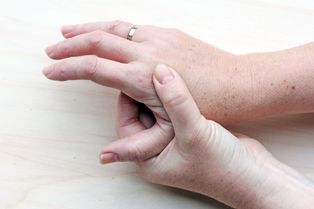
Rheumatoid arthritis is generally known as a chronic inflammatory disorder which can affect not only the joints. In some individual, rheumatoid arthritis has been found to damage a wide range of body systems, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease which occurs when the immune system erroneously attacks the tissues of your own body.
Unlike damage caused by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of the joints and causes a painful swelling that ultimately can lead to bone erosion and joint deformation.
The inflammation which is associated with rheumatoid arthritis can also damage other parts of the body. Although newer types of medicines have significantly improved treatment options, severe rheumatoid arthritis can still cause physical disabilities.
What are the Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The attack of the immune system on the synovium which is the lining of the membranes that surrounds the joint causes rheumatoid arthritis.
The synovium becomes thicker due to the resulting inflammation, this may eventually destroy the cartilage and bone in the joint.
Both the tendons and ligaments which hold the joint together becomes weak and stretch. The joint loses its shape and alignment through a gradual process.
What actually causes this process is not known by physicians, even if it seems that there is a genetic component. Although your genes do not actually cause rheumatoid arthritis, they can make you more susceptible to environmental factors such as infections by certain viruses and bacteria that can cause the disease.
Risk Factors
Below are the lists of factors that can increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis:
1. Sex. Women are at higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis than men.
2. Age. Rheumatoid arthritis may occur at any age but most often begins between 40 and 60 years of age.
3. Family history. In the event that a family member has rheumatoid arthritis, you may have an increased risk of contracting this disease as it can be inherited.
4. Smoking. One of those things that increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis is the smoking of cigarette, especially if you have a genetic predisposition to developing the disease. Smoking seems to be related to the severity of the disease.
5. Exposure to the environment. Although this has not been proofed to be certain and understood, some exposure to asbestos or silica may increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
6. Obesity. Individuals who are overweight or obesity seem to have a higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, especially in women with a diagnosis of a disease at the age of 55 or younger.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic or long-lasting disease characterized by symptoms of inflammation and joint pain. These symptoms and signs appear during a period referred to as flares. Other times are known as remission periods - that's when the symptoms are completely scattered. Signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may include: • Tender, warm, swollen joints • Stiffness at the joint which is considered to be worse in the mornings and after inactivity • Fatigue, fever and weight loss Early rheumatoid arthritis usually affects your small joints - especially the joints which connect your fingers to your arms and the toes to the feet. As the disease progresses, the symptoms often spread to the wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, hips, and shoulders. In most cases, symptoms appear in the same joints on both sides of your body. About 40% of people with rheumatoid arthritis have signs and symptoms that do not affect the joints.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis requires restoring the circulation and blood flow to the affected structures in your arthritic area. Pain is caused when swelling, inflammation and decreased circulation generate a blockage, which causes blood flow to be interrupted or slowed. Treatment for this issue requires breaking up the accumulated fluids in your arthritic area to allow for improved healing and quicker recovery.
Products recommended for symptoms of swelling, redness, pain, and inflammation, and if coolness makes your pain feel better:
Ice Substitute Poultice
Bruise Relief Liniment
Muscle Therapy Massage Oil
Products recommended when swelling and inflammation are gone, but you still feel pain, stiffness, weakness, and/or sensitivity in cold and damp weather, and if heat makes your pain feel better:
Pain Relief Liniment
Tendon and Ligament Poultice
Muscle Therapy Massage Oil
